Introduction
In critical environments, controlling static electricity is essential. ESD Gloves are a vital tool in cleanrooms and static-sensitive industries. They protect sensitive components, prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD), and maintain contamination control.
This post will guide you on how to choose and use anti-static work gloves across different industries. We will explore key features, application tips, and industry-specific selection advice.
What Are ESD Gloves?
ESD Gloves are designed to prevent the buildup and discharge of static electricity. They often use conductive fibers woven into the glove material, such as carbon, copper, or silver.
Key features include:
-
Static dissipation
-
Low particle generation
-
Good dexterity and tactile sensitivity
-
Durability against chemicals and abrasion
These gloves are critical in electronics, pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and aerospace industries.

Why Use ESD Gloves in Cleanrooms?
Protect Sensitive Components
Electrostatic discharge can damage microchips, sensors, and other delicate parts. Anti-static gloves protect both the worker and the component.
Maintain Cleanroom Integrity
Standard gloves may generate particles. Cleanroom-rated anti-static gloves are specially processed to reduce shedding and contamination.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Many industries require ESD control measures according to ISO, GMP, or IEC standards.
Keywords: anti-static work gloves, ESD gloves, cleanroom gloves, static control gloves
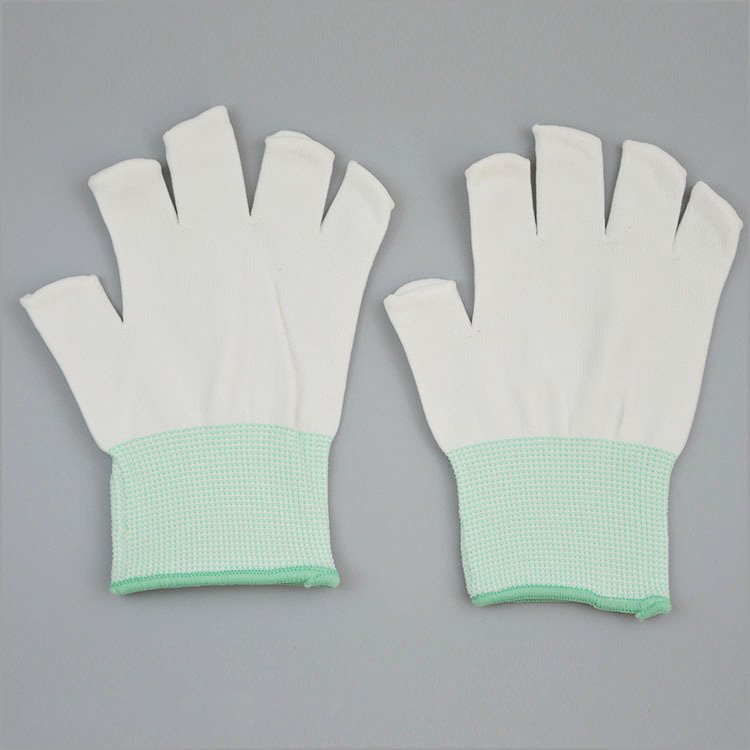

Key Types of Anti-Static Work Gloves
1. Polyester Carbon Gloves
-
Made from polyester and carbon filament
-
Lightweight and breathable
-
Excellent for electronics assembly and inspection tasks
2. Nylon ESD Gloves
-
Made from nylon with conductive fibers
-
Durable with strong stretch
-
Great for semiconductor manufacturing and lab work
3. Nitrile ESD Gloves
-
Nitrile coating enhances chemical resistance
-
Ideal for handling solvents and chemical processes
4. PU-Coated Anti-Static Gloves
-
Polyurethane (PU) coating on fingertips or palms
-
Provides grip and precision
-
Suitable for small parts assembly
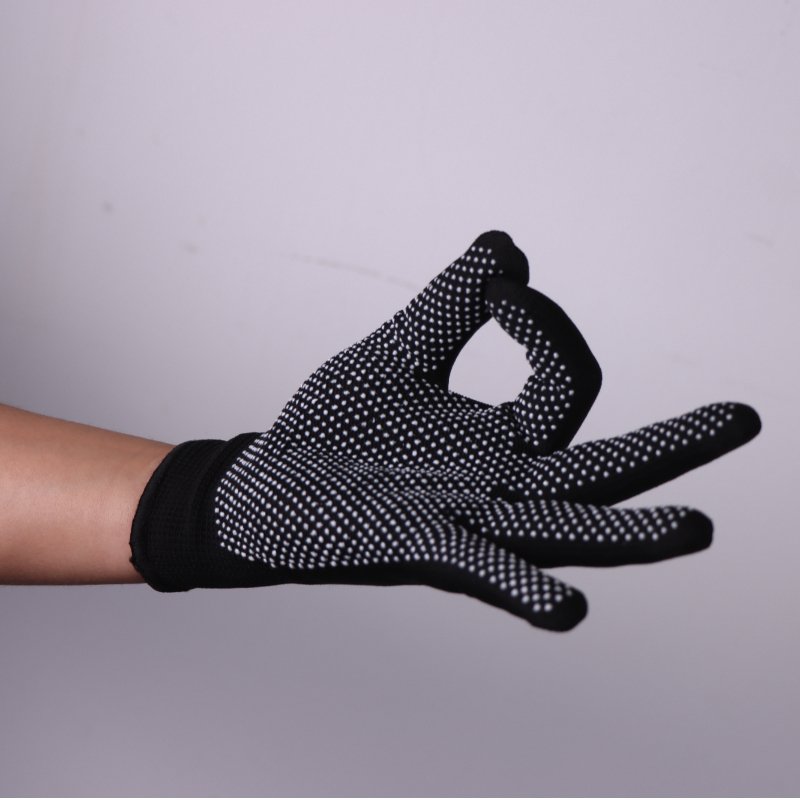

How to Choose the Right Anti-Static Work Gloves
1. Assess Cleanroom Class
-
ISO Class 3–5: Require ultra-low lint gloves like polyester carbon gloves.
-
ISO Class 6–8: Can use standard ESD nylon gloves.
2. Understand the Application
-
Fine Assembly: Use thin PU-coated gloves for tactile sensitivity.
-
Chemical Handling: Choose nitrile-based gloves for chemical resistance.
-
General ESD Protection: Nylon ESD gloves are suitable for basic tasks.
3. Consider Comfort and Fit
-
Choose gloves with proper sizing to avoid fatigue.
-
Breathable materials are important for long hours.
4. Check for Certifications
Look for:
-
ESD compliance (ANSI/ESD S20.20)
-
Cleanroom compatibility (ISO 14644)
Keywords: choosing anti-static gloves, cleanroom ESD gloves, best anti-static work gloves
Industry Applications of Anti-Static Work Gloves
1. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
In electronics manufacturing, gloves must prevent static buildup without shedding fibers. Polyester carbon gloves and PU-coated gloves are ideal here.
Tasks include:
-
PCB assembly
-
IC chip handling
-
Quality control inspections
2. Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
Cleanrooms in pharmaceuticals demand gloves with:
-
ESD protection
-
Low particle generation
-
Chemical resistance
Nitrile ESD gloves work best, especially for sterile environments.
3. Aerospace and Defense
Precision and static protection are critical. Use nylon ESD gloves for wiring and assembly of sensitive aerospace parts.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing
Manufacturing implantable devices or diagnostic tools requires gloves that:
-
Control static
-
Maintain cleanliness
-
Offer fine dexterity
PU-coated ESD gloves are often preferred.
5. Automotive Electronics
Modern cars have many sensitive electronic modules. Technicians should wear anti-static gloves during:
-
Sensor installation
-
ECU programming
-
Battery work
Best Practices for Using Anti-Static Work Gloves
1. Correct Wearing Method
-
Fully cover wrists to ensure grounding.
-
Avoid touching external surfaces that can recharge static.
2. Regular Inspection
-
Check gloves for holes, tears, or wear.
-
Replace damaged gloves immediately.
3. Proper Storage
-
Store in clean, dry, and static-free areas.
-
Avoid contamination before use.
4. Cleaning and Reuse
-
Some gloves are washable under controlled methods.
-
Always follow manufacturer instructions if reusing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Using standard gloves thinking they are ESD-safe
-
Reusing dirty or torn gloves
-
Wearing gloves without a wrist grounding strap (in some cases)
-
Using incompatible gloves for cleanroom environments
OEM & ODM Solutions for Gloves
We provide:
-
Custom sizes and materials
-
Private labeling
-
Bulk supply for industrial projects
-
Custom cleanroom packaging options
Partner with us for OEM/ODM anti-static glove manufacturing tailored to your needs!
Conclusion
Choosing and using the right anti-static work gloves is crucial in cleanroom applications. It protects sensitive products, ensures regulatory compliance, and maintains workplace safety.
Whether you are in electronics, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, or automotive industries, understanding glove types, features, and proper use will improve your ESD control measures.
Looking for a trusted supplier of cleanroom anti-static gloves? Contact us today for consultation and bulk pricing!





-3.jpg)
-4.jpg)

